Python字典
在本教程中,您将了解有关 Python 字典的所有内容;它们是如何创建的,访问,添加,从中删除元素以及各种内置方法。
Python 字典是一个无序的项目集合。字典的每一项都有key/value键值对。
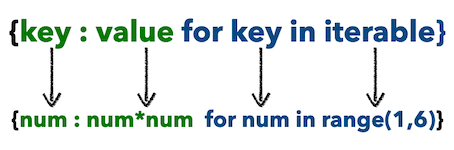
创建Python字典
创建字典就像将项目放在{}用逗号分隔的花括号内一样简单。
一个项目有一个key和一个对应value的表示为一对(键:值)。虽然值可以是任何数据类型并且可以重复,但键必须是不可变类型(字符串、数字或具有不可变元素的元组)并且必须是唯一的。可参考:Python基础 基本数据类型
# empty dictionary
my_dict = {}
# dictionary with integer keys
my_dict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'}
# dictionary with mixed keys
my_dict = {'name': 'John', 1: [2, 4, 3]}
# using dict()
my_dict = dict({1:'apple', 2:'ball'})
# from sequence having each item as a pair
my_dict = dict([(1,'apple'), (2,'ball')]) 从上面可以看出,我们还可以使用内置dict()函数创建字典。
从字典访问元素
虽然索引与其他数据类型一起使用来访问值,但字典使用keys. 键可以在方括号内使用,也可以[]与get()方法一起使用。如果我们使用方括号[ ],KeyError则在字典中找不到键的情况下引发。另一方面,如果未找到密钥,则该get()方法返回None。
# get vs [] for retrieving elements
my_dict = {'name': 'Jack', 'age': 26}
# Output: Jack
print(my_dict['name'])
# Output: 26
print(my_dict.get('age'))
# Trying to access keys which doesn't exist throws error
# Output None
print(my_dict.get('address'))
# KeyError
print(my_dict['address'])输出
Jack
26
None
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<string>", line 15, in <module>
print(my_dict['address'])
KeyError: 'address'更改和添加字典元素
字典是可变的。我们可以使用赋值运算符添加新项目或更改现有项目的值。如果键已经存在,则现有值会被更新。如果键不存在,一个新的(键:值)对被添加到字典中。
# Changing and adding Dictionary Elements
my_dict = {'name': 'Jack', 'age': 26}
# update value
my_dict['age'] = 27
#Output: {'age': 27, 'name': 'Jack'}
print(my_dict)
# add item
my_dict['favorite_book'] = 'WordPress建站'
# Output: {'favorite_book': 'WordPress建站', 'age': 27, 'name': 'Jack'}
print(my_dict)输出
{'name': 'Jack', 'age': 27}
{'name': 'Jack', 'age': 27, 'favorite_book': 'WordPress建站'}从字典中删除元素
我们可以使用pop()方法删除字典中的特定项目。此方法删除具有提供的项目key并返回value。
该popitem()方法可用于(key, value)从字典中返回并删除字典中的最后一个键值对,如果字典已经为空,却调用了此方法,就报出 KeyError 异常。使用该clear()方法可以一次删除所有项目。我们还可以使用del关键字来删除单个项目或整个字典本身。参考官网了解更多python字典方法
# Removing elements from a dictionary
# create a dictionary
squares = {1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 9, 4: 16, 5: 25}
# remove a particular item, returns its value
# Output: 16
print(squares.pop(4))
# Output: {1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 9, 5: 25}
print(squares)
# remove an arbitrary item, return (key,value)
# Output: (5, 25)
print(squares.popitem())
# Output: {1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 9}
print(squares)
# remove all items
squares.clear()
# Output: {}
print(squares)
# delete the dictionary itself
del squares
# Throws Error
print(squares)输出
16
{1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 9, 5: 25}
(5, 25)
{1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 9}
{}
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<string>", line 30, in <module>
print(squares)
NameError: name 'squares' is not definedPython字典方法
以下列出了可用于字典的方法。其中一些已经在上面的例子中使用过。

这些方法的一些示例用例:
# Dictionary Methods
marks = {}.fromkeys(['Pycharm教程', 'Astra教程', 'Genesis教程'], 0)
# Output: {'Pycharm教程': 0, 'Astra教程': 0, 'Genesis教程': 0}
print(marks)
for item in marks.items():
print(item)
# Output: ['English', 'Math', 'Science']
print(list(sorted(marks.keys())))输出
{'Pycharm教程': 0, 'Astra教程': 0, 'Genesis教程': 0}
('Pycharm教程': 0)
('Astra教程': 0)
('Genesis教程': 0)
['Pycharm教程'、 'Astra教程'、'Genesis教程']字典成员测试
我们可以用 in 来测试 key 关键字是否在在字典中。请注意,成员资格测试仅适用于keys而不适用于values。
# Membership Test for Dictionary Keys
squares = {1: 1, 3: 9, 5: 25, 7: 49, 9: 81}
# Output: True
print(1 in squares)
# Output: True
print(2 not in squares)
# membership tests for key only not value
# Output: False
print(49 in squares)输出
True
True
False遍历字典
我们可以使用循环遍历字典中的每个键for。
# Iterating through a Dictionary
squares = {1: 1, 3: 9, 5: 25, 7: 49, 9: 81}
for i in squares:
print(squares[i])输出
1 9 25 49 81
python字典内置函数
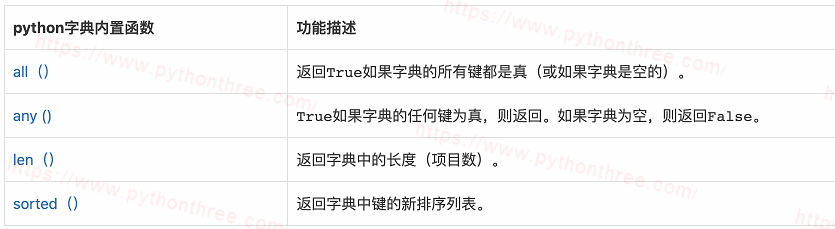
内置函数all(),any(),len(),sorted(),等。通常使用字典用于执行不同的任务。
下面是一些使用内置函数处理字典的示例。
# Dictionary Built-in Functions
squares = {0: 0, 1: 1, 3: 9, 5: 25, 7: 49, 9: 81}
# Output: False
print(all(squares))
# Output: True
print(any(squares))
# Output: 6
print(len(squares))
# Output: [0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
print(sorted(squares))输出
False True 6 [0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9]









