Python关键字
Python关键字也称为保留字。python解释器使用它们来理解程序。关键字定义程序的结构。我们不能使用关键字来命名程序实体,例如变量、类和函数。保留字(关键字)是用语言中预定义的含义和语法定义的。这些关键字必须用于开发编程指令。保留字不能用作其他编程元素(如变量名、函数名等)的标识符。本文晓得博客为你介绍Python关键字。

Python中有多少关键字?
Python 有很多关键字。随着Python中新功能的加入,这个数字还在不断增长。Python 3.8.7 是编写本教程时的当前版本,有 35个python关键字。以下是 Python3中的保留关键字列表
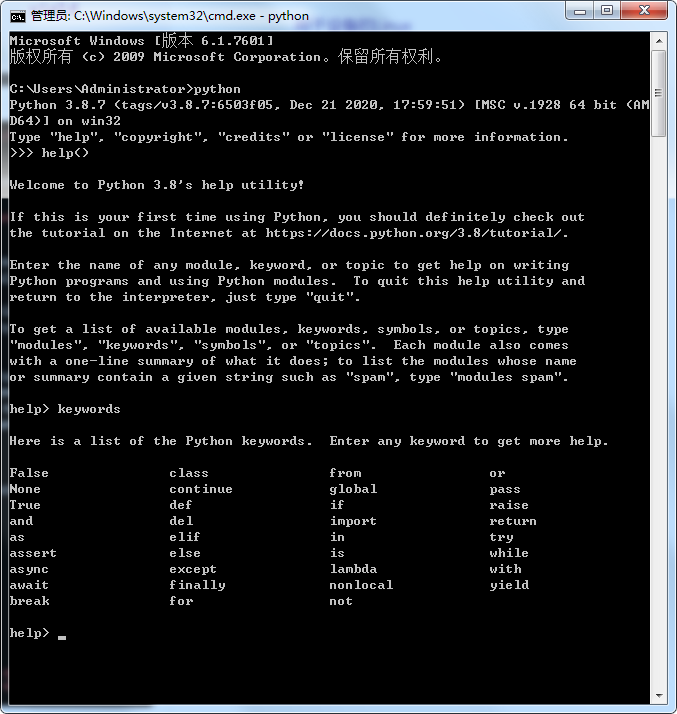
PS C:\Users\Administrator\PycharmProjects\pythonProject3> python
Python 3.8.7 (tags/v3.8.7:6503f05, Dec 21 2020, 17:59:51) [MSC v.1928 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> help()
Welcome to Python 3.8's help utility!
If this is your first time using Python, you should definitely check out
the tutorial on the Internet at https://docs.python.org/3.8/tutorial/.
Enter the name of any module, keyword, or topic to get help on writing
Python programs and using Python modules. To quit this help utility and
return to the interpreter, just type "quit".
To get a list of available modules, keywords, symbols, or topics, type
"modules", "keywords", "symbols", or "topics". Each module also comes
with a one-line summary of what it does; to list the modules whose name
or summary contain a given string such as "spam", type "modules spam".
help> keywords
Here is a list of the Python keywords. Enter any keyword to get more help.
False class from or
None continue global pass
True def if raise
and del import return
as elif in try
assert else is while
async except lambda with
await finally nonlocal yield
break for not
help>
我们可以使用 python 解释器帮助实用程序获取python关键字的完整列表。
Python关键字简介
下面我们晓得博客简单介绍python关键字的目的和用法的基本概念。
| 序号 | 关键字 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | False | 布尔值,比较运算的结果 | x = False |
| 2 | class | 定义类 | class Foo: pass |
| 3 | from | 导入模块的特定部分 | from collections import OrderedDict |
| 4 | or | 逻辑运算符 | x = True or False |
| 5 | None | 表示 null 值 | x = None |
| 6 | continue | 继续循环的下一个迭代 | numbers = range(1,11) for number in numbers: if number == 7: continue |
| 7 | global | 声明全局变量 | x = 0 def add(): global x x = x + 10 add() print(x) # 10 |
| 8 | pass | null 语句,一条什么都不做的语句 | def foo(): pass |
| 9 | True | 布尔值,比较运算的结果 | x = True |
| 10 | def | 定义函数 | def bar(): print(“Hello”) |
| 11 | if | 写一个条件语句 | x = 10 if x%2 == 0: print(“x is even”) # prints “x is even” |
| 12 | raise | 产生异常 | def square(x): if type(x) is not int: raise TypeError(“Require int argument”) print(x * x) |
| 13 | and | 逻辑运算符 | x = True y = Falseprint(x and y) # False |
| 14 | del | 删除对象 | s1 = “Hello” print(s1) # Hello del s1 print(s1) # NameError: name ‘s1’ is not defined |
| 15 | import | 导入模块 | # importing class from a module from collections import OrderedDict# import module import math |
| 16 | return | 退出函数并返回值 | def add(x,y): return x+y |
| 17 | as | 创建别名 | from collections import OrderedDict as od import math as mwith open(‘data.csv’) as file: pass # do some processing on filetry: pass except TypeError as e: pass |
| 18 | elif | 在条件语句中使用,等同于 else if | x = 10if x > 10: print(‘x is greater than 10’) elif x > 100: print(‘x is greater than 100’) elif x == 10: print(‘x is equal to 10’) else: print(‘x is less than 10’) |
| 19 | in | 检查列表、元组等集合中是否存在某个值 | l1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]if 2 in l1: print(‘list contains 2’)s = ‘abcd’if ‘a’ in s: print(‘string contains a’) |
| 20 | try | 编写 try…except 语句 | x = ” try: i = int(x) except ValueError as ae: print(ae)# invalid literal for int() with base 10: ” |
| 21 | assert | 用于调试 | def divide(a, b): assert b != 0 return a / b |
| 22 | else | 用于条件语句 | if False: pass else: print(‘this will always print’) |
| 23 | is | 测试两个变量是否相等 | fruits = [‘apple’] fruits1 = [‘apple’] f = fruits print(f is fruits) # True print(fruits1 is fruits) # False |
| 24 | while | 创建 while 循环 | i = 0 while i < 3: print(i) i+=1# Output # 0 # 1 # 2 |
| 25 | async | Python 3.5 中引入的新关键字。 用在协程函数体中。 与 async 模块和 await 关键字一起使用。 | import asyncio import timeasync def ping(url): print(f’Ping Started for {url}’) await asyncio.sleep(1) print(f’Ping Finished for {url}’)async def main(): await asyncio.gather( ping(‘askpython.com’), ping(‘python.org’), )if __name__ == ‘__main__’: then = time.time() loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(main()) now = time.time() print(f’Execution Time = {now – then}’)# Output Ping Started for askpython.com Ping Started for python.org Ping Finished for askpython.com Ping Finished for python.org Execution Time = 1.004091739654541 |
| 26 | await | Python3.5中用于异步处理的关键字 | Above example demonstrates the use of async and await keywords. |
| 27 | lambda | 创建匿名函数 | multiply = lambda a, b: a * b print(multiply(8, 6)) # 48 |
| 28 | with | 用于简化异常处理 | with open(‘data.csv’) as file: file.read() |
| 29 | except | 处理异常,发生异常时如何执行 | Please check the try keyword example. |
| 30 | finally | 处理异常,无论是否存在异常,都将执行一段代码 | def division(x, y): try: return x / y except ZeroDivisionError as e: print(e) return -1 finally: print(‘this will always execute’)print(division(10, 2)) print(division(10, 0))# Output this will always execute 5.0 division by zero this will always execute -1 |
| 31 | nonlocal | 声明非局部变量 | def outer(): v = ‘outer’def inner(): nonlocal v v = ‘inner’inner() print(v)outer() |
| 32 | yield | 结束函数,返回生成器 | def multiplyByTen(*kwargs): for i in kwargs: yield i * 10a = multiplyByTen(4, 5,) # a is generator object, an iterator# showing the values for i in a: print(i)# Output 40 50 |
| 33 | break | 跳出循环 | number = 1 while True: print(number) number += 2 if number > 5: break print(number) # never executed# Output 1 3 5 |
| 34 | for | 创建 for 循环 | s1 = ‘Hello’ for c in s1: print(c)# Output H e l l o |
| 35 | not | 逻辑运算符 | x = 20 if x is not 10: print(‘x is not equal to 10’)x = True print(not x) # False |