Python循环设计
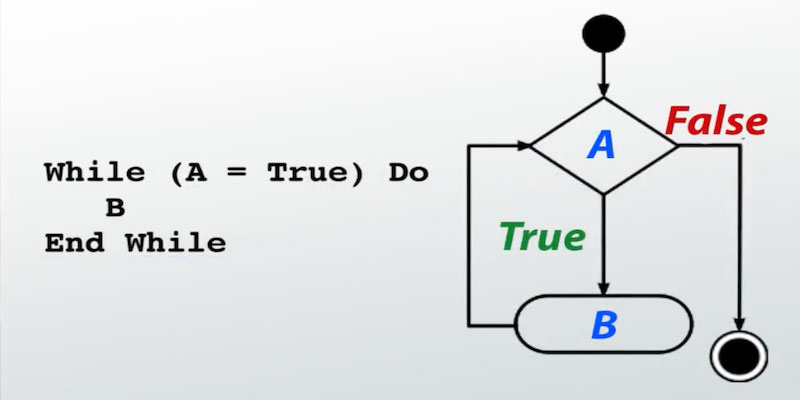
Python 编程提供了两种循环,for 循环 和while 循环。将这些循环与诸如 break 和 continue 之类的循环控制语句一起使用,我们可以创建各种形式的Python循环设计。在本文中,晓得博客将带你了解使用诸如 break 和 continue 之类的循环控制语句来控制Python循环设计。
使用 while 的无限循环
我们可以使用 while 语句创建一个无限循环。如果 while 循环的条件总是True,我们就会得到一个无限循环。
# An example of infinite loop
# press Ctrl + c to exit from the loop
while True:
num = int(input("Enter an integer: "))
print("The double of",num,"is",2 * num)
输出
Enter an integer: 3 The double of 3 is 6 Enter an integer: 5 The double of 5 is 10 Enter an integer: 6 The double of 6 is 12 Enter an integer: Traceback (most recent call last):
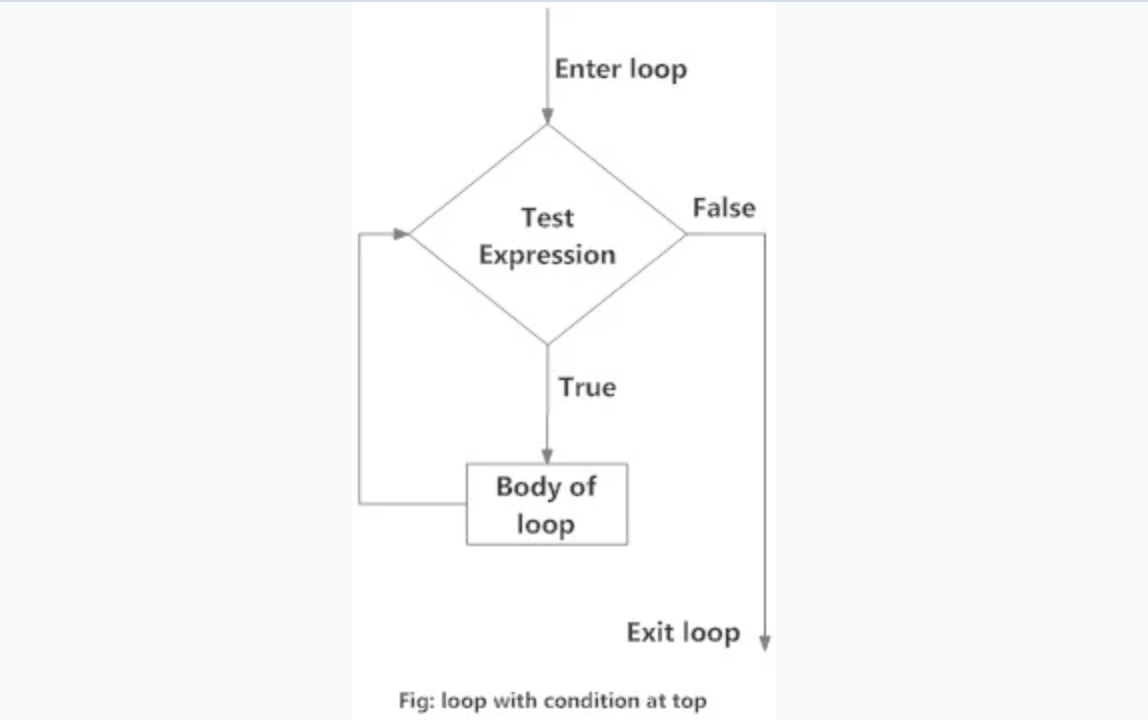
循环条件在顶部
这是一个没有 break 语句的普通 while 循环。while 循环的条件位于顶部,当该条件为 时循环终止False。可参考Python条件控制
示例:
# Program to illustrate a loop with the condition at the top
# Try different numbers
n = 10
# Uncomment to get user input
#n = int(input("Enter n: "))
# initialize sum and counter
sum = 0
i = 1
while i <= n:
sum = sum + i
i = i+1 # update counter
# print the sum
print("The sum is",sum)当你运行程序时,输出将是:
The sum is 55
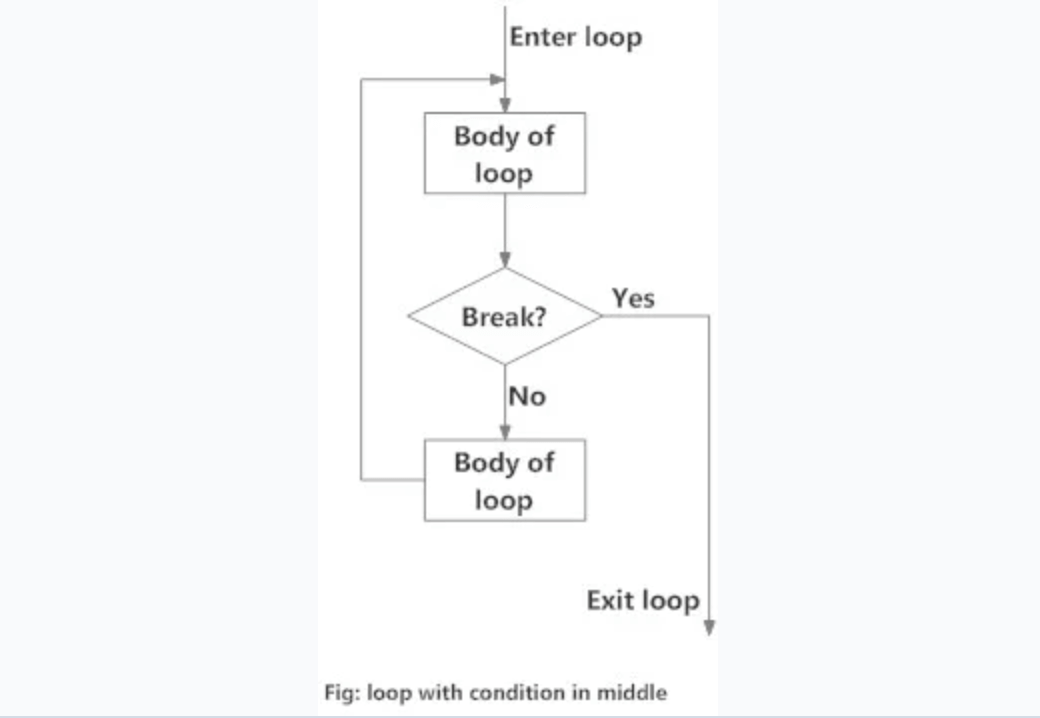
中间有条件的循环
这种循环可以使用无限循环以及循环体之间的条件中断来实现。
示例:
# Program to illustrate a loop with condition in the middle.
# Take input from the user until a vowel is entered
vowels = "aeiouAEIOU"
# infinite loop
while True:
v = input("Enter a vowel: ")
# condition in the middle
if v in vowels:
break
print("That is not a vowel. Try again!")
print("Thank you!")
输出
Enter a vowel: r That is not a vowel. Try again! Enter a vowel: 6 That is not a vowel. Try again! Enter a vowel: , That is not a vowel. Try again! Enter a vowel: u Thank you!
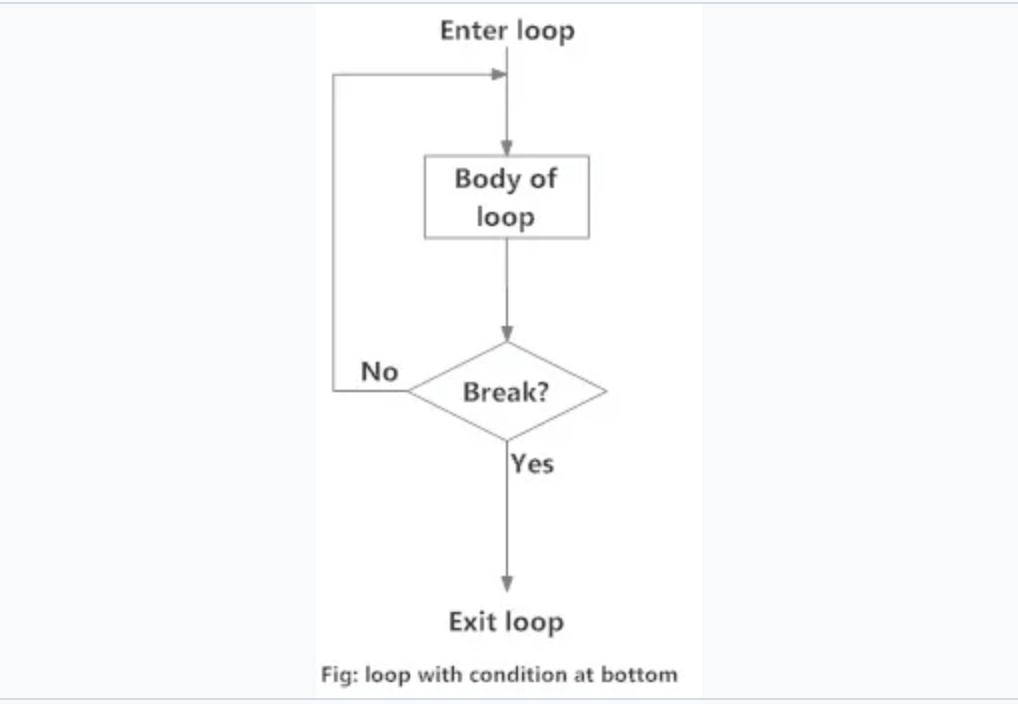
循环底部的条件
这种循环确保循环体至少执行一次。它可以使用无限循环以及最后的条件中断来实现。这类似于 C 中的 do…while 循环。
示例:
# Python program to illustrate a loop with the condition at the bottom
# Roll a dice until the user chooses to exit
# import random module
import random
while True:
input("Press enter to roll the dice")
# get a number between 1 to 6
num = random.randint(1,6)
print("You got",num)
option = input("Roll again?(y/n) ")
# condition
if option == 'n':
break
输出
Press enter to roll the dice You got 1 Roll again?(y/n) y Press enter to roll the dice You got 5 Roll again?(y/n) n
以上是晓得博客为你介绍的Python循环设计,这是基本的循环设计,当然你也可以利用Python内置函数更进一步控制程序,例如range()来控制步长,利用zip()函数接受可迭代对象,将它们聚合在一个元组中,然后返回它。









